T2I Pathophysiology
The immune system is comprised of the innate immune system, which acts as a rapid, nonspecific first line of defense against pathogens and environmental insults, and the adaptive immune system, which acts with specificity to provide a more robust and targeted response.1
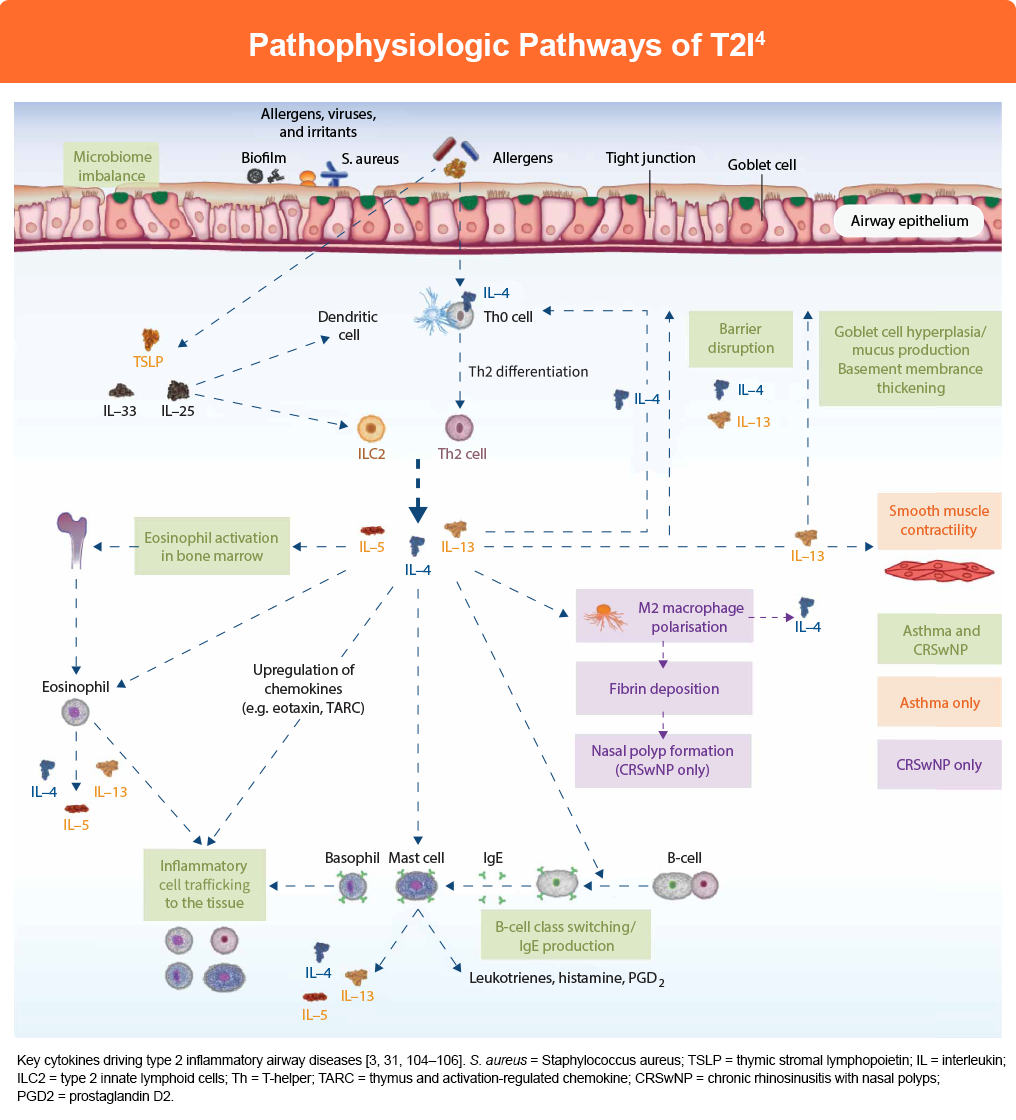
Type 2 inflammation (T2I) is driven by both the adaptive and innate arms of the immune system.1 In a typical type 2 immune response, the epithelium releases alarmins IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) on the allergen or environmental insult, initiating the type 2 response.2,3
These factors signal innate cells, including basophils, mast cells, and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), to produce and release the type 2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. IL-4 serves as a master regulator, promoting the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th2 cells that further amplify the response by producing additional IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 cytokines, creating a self-amplifying inflammatory cascade.4
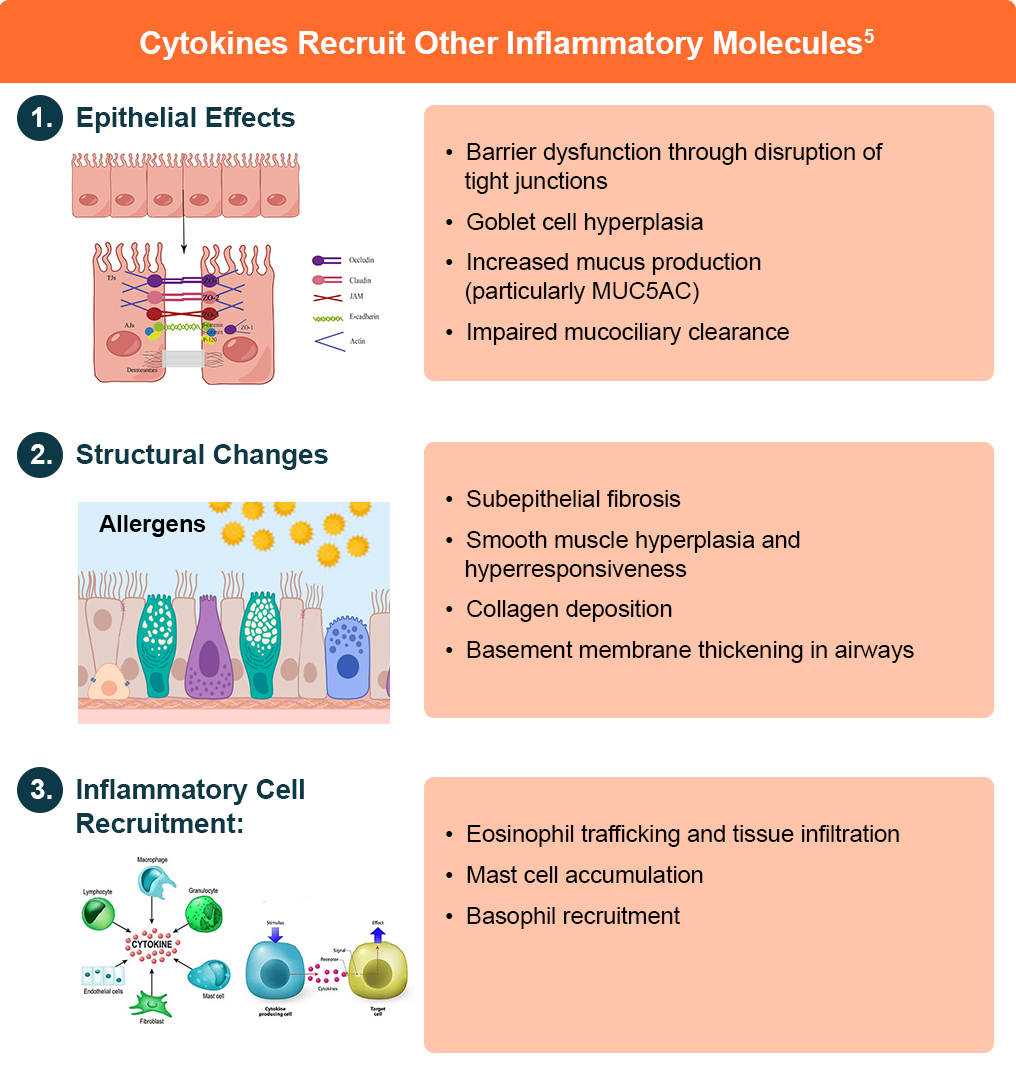
IL-4 and IL-13 share several overlapping functions due to their common receptor complex (IL-4Rα), including: 4
- B-cell class switching and IgE production
- Activation and trafficking of mast cells
- Epithelial barrier dysfunction
- Tissue remodeling and fibrosis
- Macrophage polarization to M2 phenotype
IL-5 specifically drives eosinophil differentiation, maturation, and survival in the bone marrow, while also supporting the development of other type 2 cells, including mast cells and basophils.4
The type 2 inflammatory response induces several characteristic tissue changes: 4
References
- Chehade M, Falk GW, Aceves S, et al. Examining the Role of type 2 inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022;1:720-732.
- Gandhi NA, Bennett BL, Graham NM, Pirozzi G, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:35-50.
- Gieseck RL, 3rd, Wilson MS, Wynn TA. Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:62-76.
- Maspero J, Adir Y, Al-Ahmad M, et al. Type 2 inflammation in asthma and other airway diseases. ERJ Open Res. 2022;8:00576-2021.
- Lu HF, Zhou YC, Yang LT, et al. Involvement and repair of epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1348272.
- Ricciardolo FLM, Guida G, Bertolini F, Di Stefano A, Carriero V. Phenotype overlap in the natural history of asthma. Eur Respir Rev. 2023;32(168):220201.
- Aryal S. Cytokines–mechanism of action and functions. Microbe Notes. May 9, 2022. https://microbenotes.com/cytokines-mechanism-of-action-and-functions/. Accessed January 23, 2025.